
Sea Level Rise

Credit: NOAA
Global sea level rise is the most obvious sign of climate change in the ocean and along the coast. This change poses a significant threat to California's 1100-mile coastline, whose counties are home to over two-thirds of the state's population, and boasts the largest ocean economy in the nation. For more information, download the Sea Level Rise chapter.
What does this indicator show?
Annual mean sea level trends
The graph shows the relative change, in millimeters, in sea levels at Crescent City (1933-2024), San Francisco (1900-2024), and La Jolla (1925-2024).
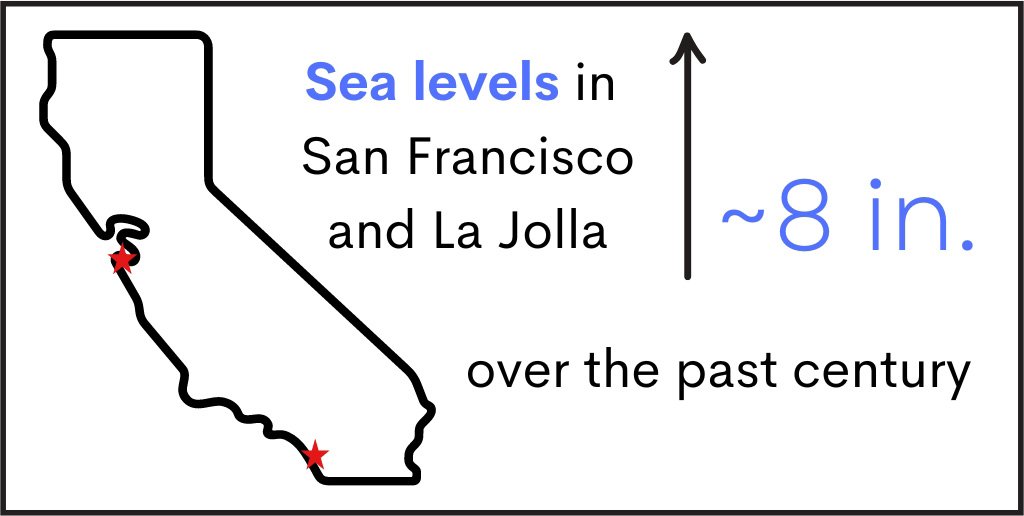
- Sea levels have increased over the past century by about 200 millimeters (mm) or 8 inches (″) in San Francisco and La Jolla.
- Sea levels have risen at other locations along the California coast except for Crescent City in northern California, where it has dropped by about 0.8 mm or 0.03″ each year. At this location, the coastline is rising faster than the sea level due to the movement of the Earth’s plates. However, projected sea level rise is expected to outpace vertical land motion in Crescent City, leading to higher sea levels.
Why is this indicator important?
- Rising sea levels pose major threats to millions of residents, infrastructure, housing, natural resources, and economies in low-lying coastal areas. Climate-driven sea level rise and storms magnify coastal hazards such as flooding, beach erosion, cliff retreat, and shallow groundwater, resulting in damages to infrastructure and loss of ecosystems. Sea level rise hits communities already struggling to adapt to climate change the hardest, including low-income communities and communities of color, where hazardous industrial sites are often found.
- Sea level rise can also cause saltwater to infiltrate groundwater, making it unsafe for drinking. This intrusion also raises groundwater levels, increasing the risk of floods, damaging buried infrastructure (such as gas lines, underground storage tanks, and septic systems), and potentially releasing harmful contaminants.
- Coastal Tribes like the Amah Mutsun and Chumash Tribes also face unique impacts on their culture and ways of life. For example, traditional places where the Tribes used to collect shells, seaweed, and other materials are increasingly out of reach.
Cliff collapse at Isla Vista, California (taken 2005). Coastal erosion and cliff collapse threaten public safety, infrastructure, and property as they become more common with sea level rise.
Credit: Patrick Barnard, US Geological Survey
What factors influence this indicator?
- The rise of global sea levels has been primarily caused by increasing global temperatures, resulting in thermal expansion of warmer oceans and the addition of water to the ocean from melting of mountain glaciers and ice sheets. The loss of ice from Greenland and Antarctica is especially concerning as it is happening at an accelerating rate. The potential sea level rise contributions from continued melting and/or ice sheet collapse could ultimately be catastrophic for coastal communities across the globe.
Additional resources
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Sea Level Rise Viewer
- National Aeronautic and Space Administration, Global Climate Change: Vital Signs of the Plant, Rising Tides: Understanding Sea Level Rise
- National Aeronautic and Space Administration, Flooding Analysis Tool
- Point Blue Conservation Science and US Geological Survey, Our Coast Our Future
- US Geological Survey, Hazard Exposure Reporting and Analytics
- US Geological Survey, Pacific Coastal and Marine Science Center, Coastal Storm Modeling System (CoSMoS)
